Mutualism Drawing
Mutualism Drawing - Additionally, there are many types of symbiotic interactions. Web mutualism is a type of symbiotic relationship where all species involved benefit from their interactions. Web mutualism is a close, symbiotic relationship that mutually benefits two different species present in an ecosystem. Web by classifying these effects, ecologists have derived five major types of species interactions: Web mutualism is an anarchist school of thought and economic theory that advocates for workers' control of the means of production, a market economy made up of individual artisans and workers' cooperatives, and occupation and use property rights. Mutualisms have shaped evolution in many ways, for example, animal and plant cells arose from a mutualism between different bacteria, with one forming the main cells and the other forming organelles. The termite benefits from the ability of the protists to digest cellulose. Web how does this resource excite and engage children's learning? Web many members of the prairie ecosystem, including grasshoppers, prairie dogs, jackrabbits, and bison, feed on the grass. The paramecium certainly benefits from the food synthesized by the alga. While mutualism is highly complex, it can be roughly broken down into two types of relationship. Additionally, there are many types of symbiotic interactions. Mutualisms are defined as interactions between organisms of two different species, in which each organism benefits from the interaction in some way. Now you have seen lots of examples of how mutualism works in real life.. Web mutualism is a close, symbiotic relationship that mutually benefits two different species present in an ecosystem. So let's first talk about competition which we have already talked about in other videos. Additionally, there are many types of symbiotic interactions. 57.1 w x 78.7 h x 2.4 d in Now you have seen lots of examples of how mutualism works. Symbiotic relationships in which each species benefits are mutualistic. Other types of symbiotic relationships include parasitism (where one species benefits and the other is. 57.1 w x 78.7 h x 2.4 d in Challenge your students to match together the organisms that demonstrate mutualism. Predation includes any interaction between two species in which one species benefits by obtaining resources from. Mutualistic interactions are common but sometimes rather complicated. This resource addresses the following standards: Mutualistic arrangements are most likely to develop between organisms with widely different living requirements. In this picture here, do you see competition? A symbiotic relationship between two species in which one benefits and the other is harmed It is a symbiotic relationship in which two different species interact with and in some cases, totally rely on one another for survival. Mutualisms have shaped evolution in many ways, for example, animal and plant cells arose from a mutualism between different bacteria, with one forming the main cells and the other forming organelles. These types of interaction are common. Mutualism occurs when both species in this interaction benefit. An interaction in which one organism is consumed by another These types of interaction are common and ubiquitous throughout all ecosystems, and scientists are increasingly recognizing the important role that they play. So let's first talk about competition which we have already talked about in other videos. Predation includes any interaction. Challenge your students to match together the organisms that demonstrate mutualism. It is a symbiotic relationship in which two different species interact with and in some cases, totally rely on one another for survival. Web mutualism is a type of symbiotic relationship where all species involved benefit from their interactions. While mutualism is highly complex, it can be roughly broken. An interaction in which both types of organisms benefit symbiosis: It is a symbiotic relationship in which two different species interact with and in some cases, totally rely on one another for survival. Web mutualism is a term used to describe a symbiotic relationship between two or more different species. Mutualistic interactions are common but sometimes rather complicated. 57.1 w. Web mutualism describes a type of mutually beneficial relationship between organisms of different species. A symbiotic relationship between two species in which one benefits and the other is unaffected: A symbiotic relationship between two species in which both partners benefit: There are hundreds of examples of mutualism between a heterotroph and an alga. Predation includes any interaction between two species. An interaction in which one organism is consumed by another The termite benefits from the ability of the protists to digest cellulose. Mutualism is a type of relationship between the host and a symbiont, where both organisms benefit and no one is harmed. So let's first talk about competition which we have already talked about in other videos. Additionally, there. Julius csotonyi in this session where he’ll be teaching you how to draw this amazing perennial plant and this fascinating. A symbiotic relationship between two species in which both partners benefit: Mutualism occurs when both species in this interaction benefit. There are hundreds of examples of mutualism between a heterotroph and an alga. Web how does this resource excite and engage children's learning? Web mutualism describes the ecological interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Web many members of the prairie ecosystem, including grasshoppers, prairie dogs, jackrabbits, and bison, feed on the grass. The term mutualist is used to indicate the small partner and the host are the other partners present in the mutualism. Mutualism is a type of relationship between the host and a symbiont, where both organisms benefit and no one is harmed. [2] prominent examples include most vascular plants engaged in mutualistic interactions with mycorrhizae, flowering plants. Mutualism examples show unique relationships where organisms work together for mutual benefit. Web mutualism is a type of symbiotic relationship where all species involved benefit from their interactions. The termite benefits from the ability of the protists to digest cellulose. A symbiotic relationship between two species in which one benefits and the other is unaffected: These types of interaction are common and ubiquitous throughout all ecosystems, and scientists are increasingly recognizing the important role that they play. 57.1 w x 78.7 h x 2.4 d in
Learn to Draw Mutualism Ghost Pipes and Tube Worms Sierra Club BC
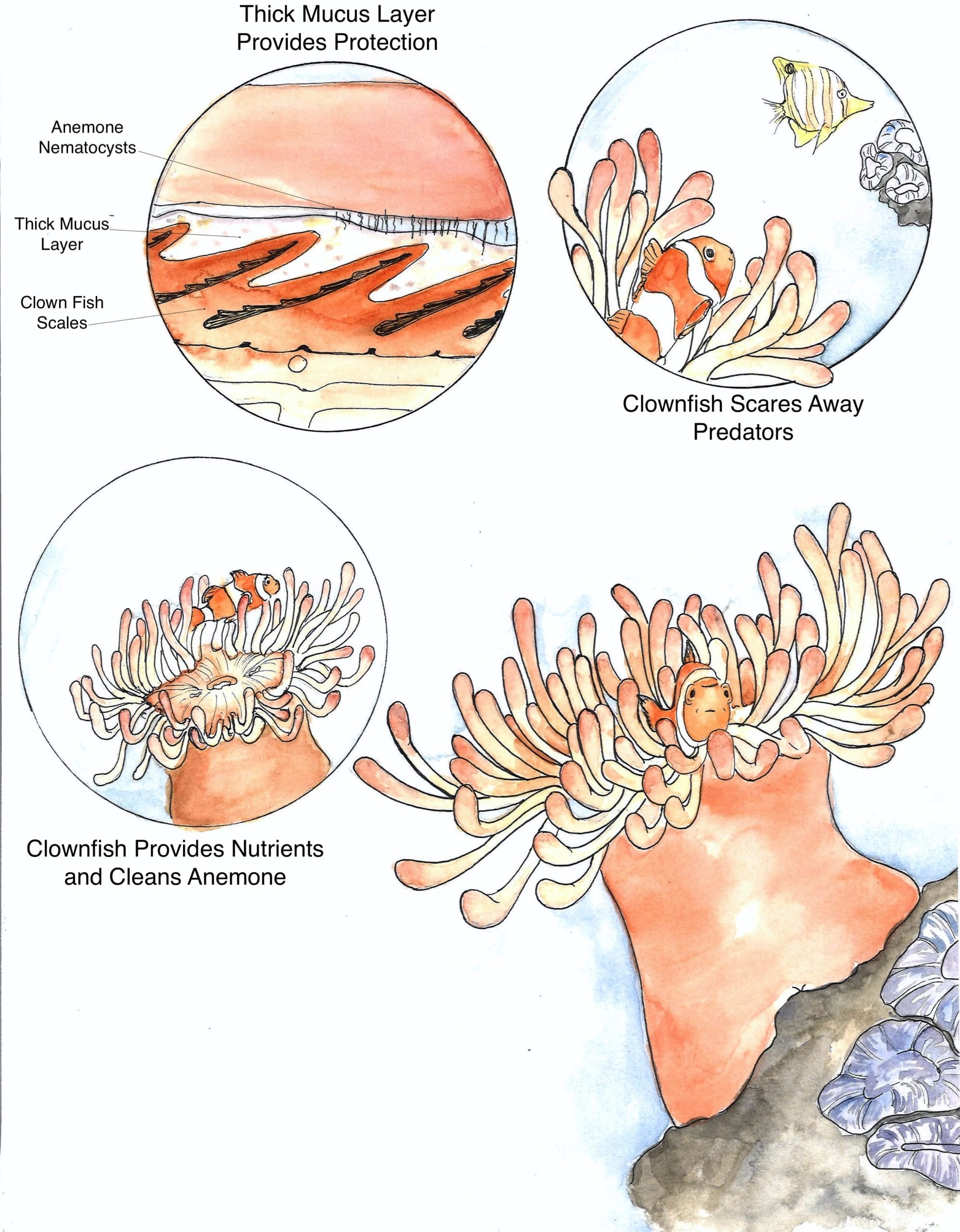
The sea anemone and the clownfish have a mutually beneficial

20_2018_Mutualism Art+Science

Mutualism MUTUALISM Mojave Desert Glossary of Terms and

Coevolution in a Mutualism Science illustration, Mutualism, Illustration

Learn to Draw Mutualism Ghost Pipes and Tube Worms Sierra Club BC

Mutualism — Definition & Examples Expii

Mutualism Coloring Page Coloring Pages
Mutualism Coloring Page Coloring Pages

Mutualism Symbiosis Mutualism Art Prints by Bonita Nurdiyanto Shop
Predation Includes Any Interaction Between Two Species In Which One Species Benefits By Obtaining Resources From And To The Detriment Of The Other.
It Is A Form Of Symbiosis That Organisms Develop For Any Of A Number Of Reasons, Including A.
Web Mutualism Describes A Type Of Mutually Beneficial Relationship Between Organisms Of Different Species.
Challenge Your Students To Match Together The Organisms That Demonstrate Mutualism.
Related Post: